Phase
Here is an oscillating ball.
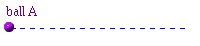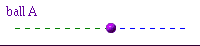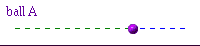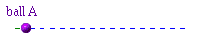
Its motion can be described as follows:
- First the ball is at v=0 at the right
- Then it moves with v<0 through the centre to the left
- Then it is at v=0 at the left
- Then it moves with v>0 through the centre to the right
- Then it repeats...
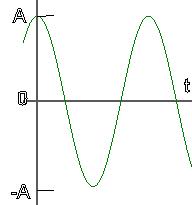
This information concentrates on what phase of the cycle is being executed. It is not concerned with the particulars of amplitude.
Mathematically, the phase is the "ωt" in:
x(t)=Acos(ωt)
The ubiquitous ball undergoes oscillations of amplitude A.
What is the phase in the following situations?
What phase is the ball in when:
x=+A, v=0
A) 0.00πrad
B) 0.25πrad
C) 0.50πrad
D) 1.0πrad
E) 1.5πrad
F.)1.7πrad
A) 0.00πrad - Correct!
B) 0.25πrad - No. Find a point where v=0 and x=A and measure how far it is from the origin
C) 0.50πrad - No. Find a point where v=0 and x=A and measure how far it is from the origin
D) 1.0πrad - No. Find a point where v=0 and x=A and measure how far it is from the origin
E) 1.5πrad - No. Find a point where v=0 and x=A and measure how far it is from the origin
F.)1.7πrad - No. Find a point where v=0 and x=A and measure how far it is from the origin
What phase is the ball in when:
x=0, v<0
A) 0.00πrad
B) 0.25πrad
C) 0.50πrad
D) 1.0πrad
E) 1.5πrad
F.)1.7πrad
A) 0.00πrad - No. You need a point where x is zero and v is negative
B) 0.25πrad - Correct!
C) 0.50πrad - No. You need a point where x is zero and v is negative
D) 1.0πrad - No. You need a point where x is zero and v is negative
E) 1.5πrad - No. You need a point where x is zero and v is negative
F.) 1.7πrad - No. You need a point where x is zero and v is negative