Newton's Laws 1
- The acceleration of an object which is free to fall in a vacuum is ...
(A) equal to the product of force and mass.
(B) proportional to the mass of the object.
(C) independent to the mass of the object.
(D) proportional to the inverse of the mass of the object.Correct = C
There is no air resistance (frictional forces) acting on falling bodies in a vacuum. As a result a light body (for instance a feather) and a heavy body (for instance a coin) would fall with the same acceleration, hence the acceleration is independent of the mass of a body in a vavuum.
- Two asteroids, which are 10000km apart, attract each other with a gravitational force of F. If the two asteroids move away from each other to a distance of 20000km apart, how great will the gravitational force be?
(A) 1/4F
(B) 1/2F
(C) 2F
(D) 4FCorrect = A
Gravitational Force=km1·m2/r2. If distance is doubled the term under the division line becomes 1/4(1/2×1/2=1/4). As a result, the gravitational force between the asteriods becomes a 1/4 of its original value.
- A girl and a boy pull in opposite directions on strings attached to each end of a spring balance. Each child exerts a force of 20N. What will the reading on the spring balance be?
(A) 0N
(B) 10N
(C) 20N
(D) 40NCorrect = C
Application of Newton 3: actio = reactio, accordungly the spring balance will measure 20N.
- A person standing on a scaffold lowers an object of weight 250N by means of a rope, at constant speed. If the weight of the rope is negligible, the force that the person exerts is …
(A) constant and less than 250N
(B) equal to 250N
(C) less than 250N and decreasing
(D) greater than 250NCorrect = B
No acceleration, hence F=ma is zero. The only acting force on the bucket is the force of gravity (weight) which equals 250N.
- When an apple falls from a tree, it drops to the ground because of the gravitational force between the apple and earth. F1 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the earth on the apple and F2 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the apple on the earth, then ...
(A) they have equal inertia.
(B) F1 is greater than F2.
(C) F1 is smaller than F2.
(D) F1 and F2 are equal.Correct = D
Again Newton 3: if a body A exerts a force F on a body B, then body B exerts an equal but opposite force on body A. Only in option D the forces are equal (in magnitude is missing).
- An astronaut picks up a stone on the moon and finds its mass to be 2kg. If the mass of the earth is 6 times more than the mass of the moon, what will the mass and the weight of the stone be on the earth?
Answer Mass Weight (A) 2kg 12N (B) 2kg 20N (C) 12kg 120N (D) 20kg 200N Correct = B
Mass stays the same wherever you are, 2kg on the moon will be 2kg on the earth. However the force of gravity on earth is stronger, 2kg will experience a gravitational pull of 20N, hence option B.
- Three objects of masses 0.5kg, 10kg and 3kg are suspended by a light rope as shown in the diagram below. What is the magnitude of the force acting in the rope at point D?
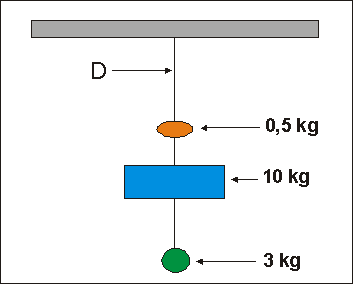
(A) 13.5N
(B) 18N
(C) 130N
(D) 135NCorrect = D
At point D the weight of all objects is acting: weight=mass (kg)×10(N/kg)=13.5×10=135N.
- An object is suspended from a spring balance in a lift. The reading of the balance is 200N when the lift is at rest. If the balance reading is 190N, the lift is moving ...
(A) downward at constant speed.
(B) downward and increasing in speed.
(C) upwards at constant speed.
(D) downward and decreasing in speed.Correct = B
At rest the object weighs 200N, the weight decreases by 10N due to acceleration (F=ma), only on accelerating downwards (option B) the weight decreases.
- The sketch shows a block of wood being dragged across a rough horizontal surface at a constant speed by a force F. The magnitude of the frictional force between the block and the surface is …
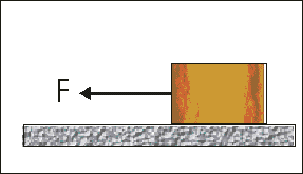
(A) zero
(B) equal to F
(C) less than F
(D) greater than FCorrect = B
Block is moving at constant speed hence acceleration is zero. Zero acceleration means frictional force is equal to pulling (or applied) force F.
- A passenger not wearing a safety belt hits the windscreen of a car in a head-on collision. This is an illustration of …
(A) Newton's First Law
(B) Newton's Second Law
(C) the Law of Conservation of Momentum
(D) Newton's Universal Law of GravitationCorrect = A
Newton 1, also known as the law of inertia: a body will remain at rest or continue with constant velocity unless acted upon by an external resultant force.

